Z-buffer 深度缓存
之前解决的是一个三角形光栅化的问题,现在要考虑多个三角形光栅化覆盖的问题
Painter’s Algorithm
(油)画家算法:由远及近画画,覆盖
- 需要对深度进行计算与排序
- 有n个三角形时,时间复杂度O(nlogn)
- 可能有无法排序的情况:例如三个三角形互相重叠
Z-buffer
Idea
- Store current min. z-value for each sample (pixel)
- Needs an additional buffer for depth values
- frame buffer stores color values
- depth buffer (z-buffer) stores depth
For simplicity we suppose z is always positive
i.e. (smaller z -> closer, larger z -> futher)
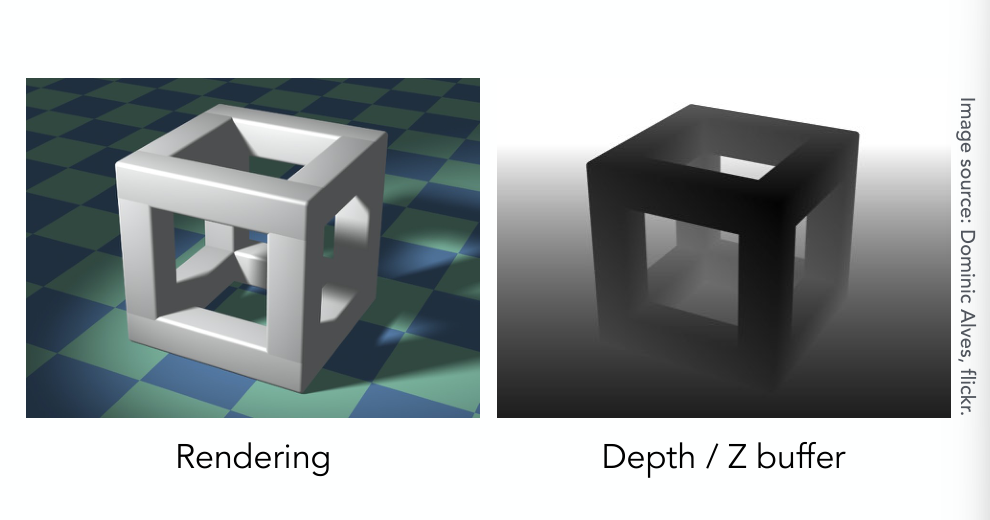
Example
把深度值转化为颜色值,近小远大,所以近处的是黑的,远处的是白的。
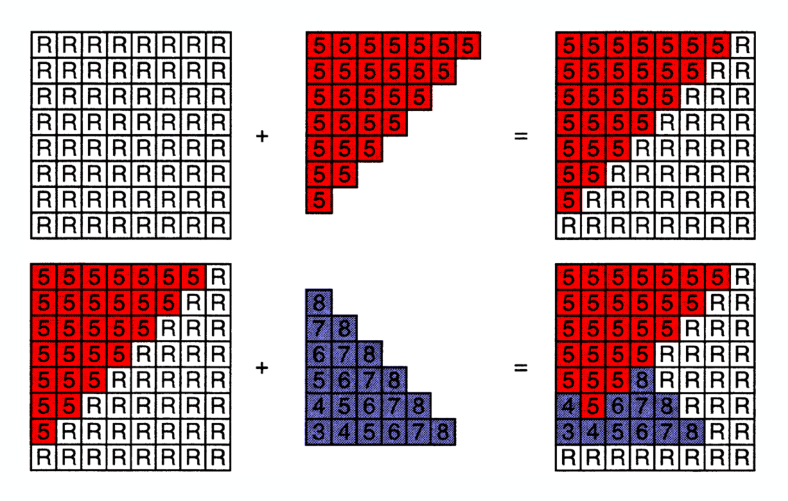
Algorithm
1 | Initialize depth buffer to ∞ |
Complexity
O(n) for n triangles(考虑每个三角形覆盖常数个像素)
不是排序算法,而是求最小值
基本上不会有两个完全相同深度的像素(浮点数不能精确的表示有理数)
假设没有相同深度的两个像素,深度缓存和画三角形的顺序无关
Most important visibility algorithm : Implemented in hardware for all GPUs
无法处理透明物体
Shading
Definition
In Merriam-Webster Dictionary
- shad·ing, [ˈʃeɪdɪŋ], noun
The darkening or coloring of an illustration or diagram with parallel lines or a block of color.
- shad·ing, [ˈʃeɪdɪŋ], noun
In this course
The process of applying a material to an object.
不同的材质和光线有不同的相互作用的方法
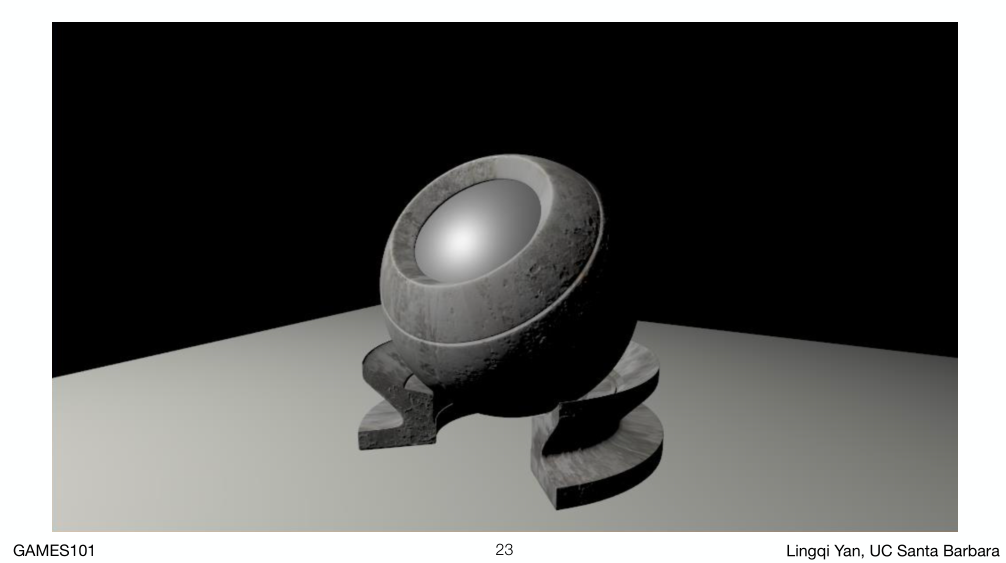
Perceptual Observations
如图所示,可以将光线简单地分为三类:
- 镜面高光
- 漫反射
- 环境光
In this course,
- 光强,光的亮度,光的能量皆指同一个概念,目前阶段暂不做区分
- 所有方向向量都为单位向量
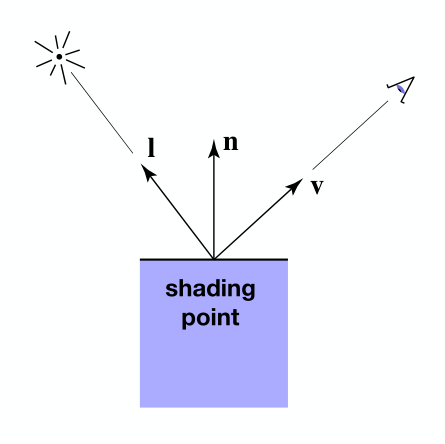
Shading is Local (局部)
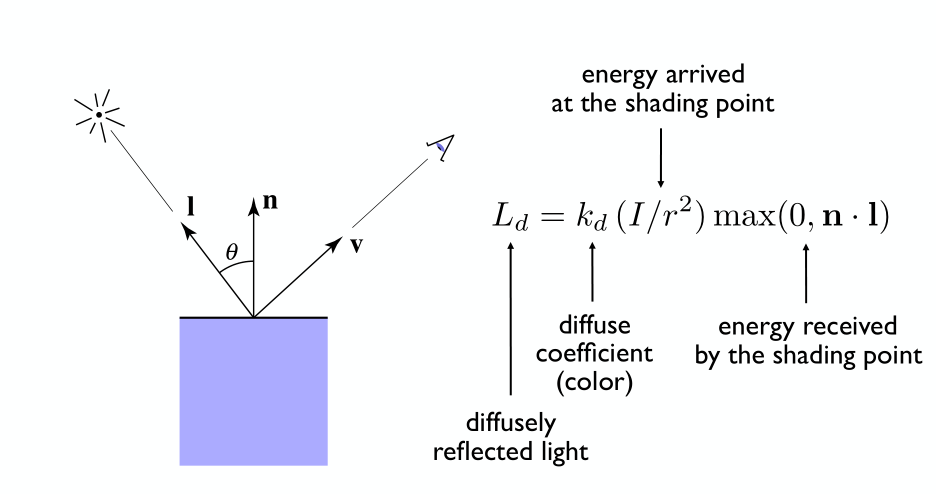
Compute light reflected toward camera at a specific shading point
Inputs:
Viewer direction, v
Surface normal, n 平面法向量
Light direction, l
(for each of many lights)
Surface parameters
(color, shininess, …)
- No shadows will be generated! (shading ≠ shadow)
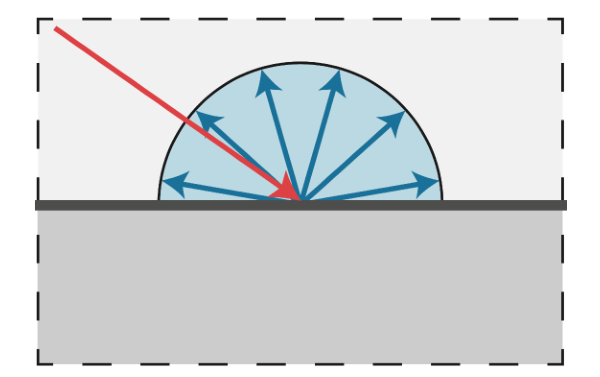
Diffuse Reflection
- Light is scattered uniformly in all directions
- Surface color is the same for all viewing directions
Lambertian (Diffuse) Shading
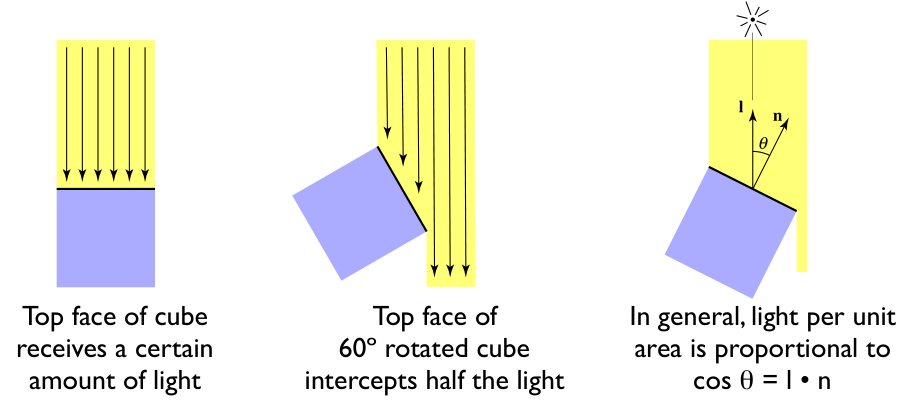
Lambert’s cosine law: how much light (energy) is received?
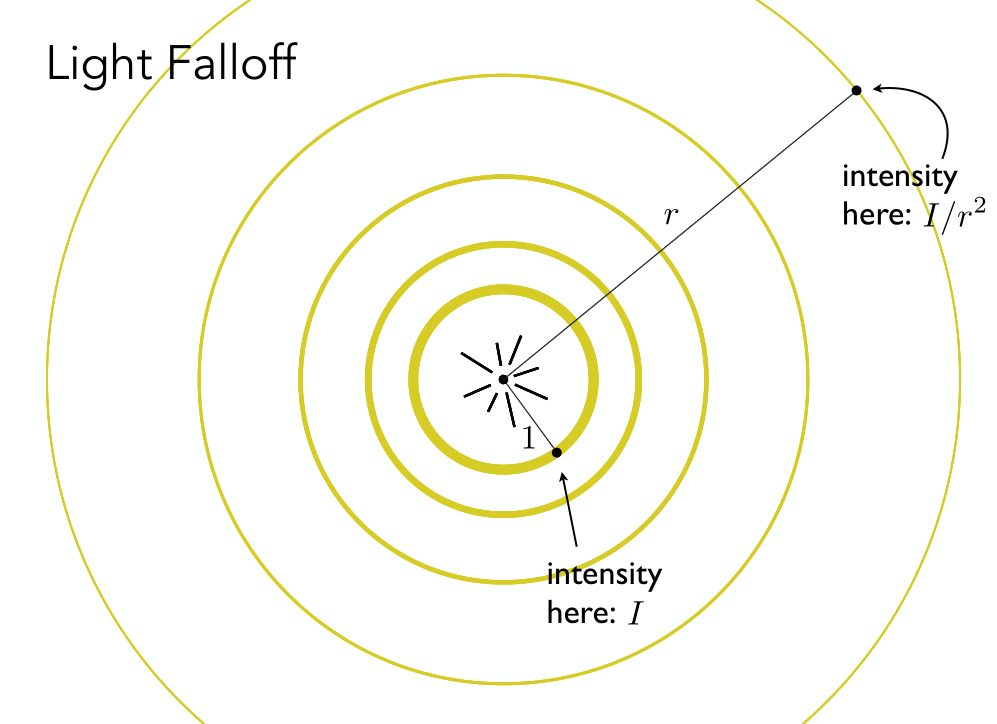
Light Falloff
想象一个逐渐扩散变大的球壳
Lambertian (Diffuse) Shading
Shading independent of view direction